PART 1: Introduction
Children with disabilities and mental disorders must attend special schools since mainstream schools are not equipped to make learning accessible to students with special needs (SENs). When regular students and SENs attend the same school, maintaining equality also becomes difficult. Therefore, our goal is to use Metaverse to deliver new opportunities for inclusive education.
Challenge of Inclusive Education
Taking HK as an example (Tait et al., 2019), in 1997, HK officially started to pilot an inclusive education policy, with schools joining voluntarily. After a survey, there were very few participating schools (most of the SENs were still educated in special education institutions) and the results were poor. The reasons for this:
- Lack of effective methods and resources: traditional methods of diversion (psychological counseling) are inefficient and increase the burden on schools.
- Teachers lack relevant training to cope with the situation.
On the other hand, in HK, most children with autism are educated in regular schools and the number is on the increase (Tait et al., 2019). The use of Metaverse in inclusive education provides effective help for SENs, such as those with autism. It also offers the possibility of teacher training.
Current Metaverse Regulations
Since metaverse technology is just starting out and has yet to mature, laws and regulations specific to the metaverse have not yet taken shape, except for those issues that can be judged by established laws, such as violence. However, technology manufacturers, academic and research institutions, government departments, and society are all involved in the discussion of rules on technology development, including safety, fairness, and the impact on social behavior and ethics.
PART 2: Ethical Debates
The digital divide is a discussion point when it comes to using the metaverse for inclusive education. Even while people from different needs might have equal opportunity to education through the metaverse, it is crucial to ensure that students have the tools that they need to engage completely, such dependable internet connection and the right gadgets. If this problem is not resolved, the metaverse may make the already-existing educational system worse.
The metaverse also presents difficulty for responsible behavior and digital ethics. Cyberbullying is a problem that may emerge as virtual worlds become more realistic and immersive. To build a welcoming learning environment, making clear rules and regulations that ensure moral behavior in the metaverse must be considered.
PART 3: Proposed Tech-powered Solution
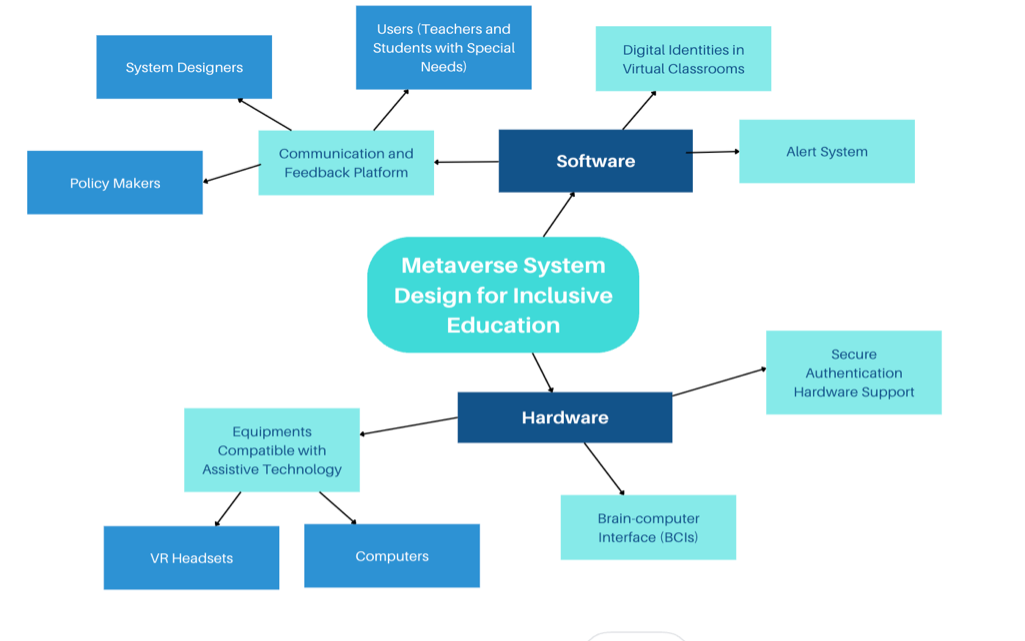
While current solutions with multiple hardware devices risk sensory overload without considering user needs, key hardware and software features have been developed including an assistive technology, virtual classroom, synced brain-computer interfaces as well as telemedicine platform to empower educational inclusion.
Hardware Requirements
- General equipment compatible with assistive technology
- VR Headsets: High-quality, affordable VR headsets suitable for children of different ages and abilities (e.g. HTC Vive, Oculus Quest)
- Computers: Desktop or laptop computers powerful enough to run VR educational software
- Assistive Devices: Tools like switches, adaptive keyboards to enable interaction for students with physical disabilities
- 3D Scanners: To assist in digitally replicating students’ environments and enabling them to attend virtually
- Cameras/Mics: For two-way video/audio interactions between virtual and physical classrooms
- Brain-computer Interface (BCIs)
BCIs allow SENs to control machines with their minds. BCIs provide new possibilities for communicating with computers in addition to speaking and typing, which not only provides new solutions for students with physical disabilities, but also allows students with mental illnesses such as locked-in syndrome to participate in metaverse dialogues and activities. BCIs enable direct communication between brains as well as the creation of brain nets for group communication, which allows disabled users to experience the entire metaverse. In addition, it is also a key technology for achieving full integration of the user with the virtual world in the long term. BCIs could simultaneously act as sensors to receive data from the virtual world and as actuators to send information.
- Secure authentication hardware support for metaverse digital identity
Secure enclaves, cryptographic hardware modules and biometric sensors ensure the integrity and confidentiality of digital identities.
Software Requirements
- Virtual Classrooms
- The digital identity system
In virtual classrooms, students embody customizable digital identity and navigate digital classrooms via virtual reality. These identities simulate real social interaction, allowing for facial expressions, body language and cues to be captured in real-time via motion sensors.
- By group User-friendly design
The interface ensures an inclusive design to accommodate diverse learners with Autism-friendly features, customizable learning paces, and alternative controllers allowing barrier-free access for mobility impairments. Text and media options also integrate screen reader support, magnification, audio descriptions and high contrast to serve visual impairments through combinatory multimedia lessons.
- Telemedicine
- Affective Computing Interface
Within virtual classrooms, an interface utilizes biosensors and brain interfaces to monitor students’ emotions, cognition, and neurological activity passively and remotely. Advanced AI analyzes these bio signals, identifying subtle changes indicating issues like psychological distress or seizures, especially for those with disabilities. Any such alerts are securely and privately sent to educators and doctors to enable immediate remote assistance or environmental adjustments.
- Healthcare
The virtual learning system includes telemedicine rooms for remote therapy sessions and physical exams via AR overlays. Mental health support encompasses virtual mindfulness areas and relaxation exercises led by avatars, assisting students in accessing counselling referrals and scheduling. Physical and nursing care also utilize interactive simulations and games to deliver patient education, exercise programs, and remote monitoring of vitals through avatars.
- Operation
- User Feedback Platform
The User Feedback Platform operates as a centralized hub – the User Experience Observatory – that facilitates open communication, collaboration and knowledge-sharing among policymakers, technology designers, teachers, and student users. It gathers comprehensive input regarding interface designs, course content, support structures, and more. Through analysis of this feedback data, new insights are generated to continuously enhance the system and optimize user experiences over time.
PART 4: Complementary Technology
- Personal Boundary and Force Quit System
- Allowing students to remain distant from other users to avoid psychological irritation
- System stopping other users from entering the student’s default boundary and alerting the student. Hence, users could only enter the boundary until when the student permits it
- Alert system notifying doctors when student experience extreme emotional response and force quit should be activated when students reach a certain severity level to protect student
- Generation emotion report of the student available on intranet among teachers and health practitioners for further medical assessment use

- Default System removing Harassing Information
- Applying of filtering and moderation technology in metaverse platforms, including chat boxes, message boards and personal blogs to block harassing information which could lead to emotional discomfort among students
- Specific application including 1) language screening 2) audio, picture and video censorship 3) recording chat log and message board
- Allowing user-generated content moderation to customize the filtering criteria of each student
- Employing machine learning algorithms for user sentiment analysis to understand behavior and language often used by each student for timely and easier identification of bullying tendencies
- Activating immediate change of victims’ virtual profile or avatar when cyberbullying is identified to protect their privacy

PART 5: Conclusion
The digital identities within the Metaverse have the potential to significantly foster inclusive education. It can provide students with different needs with equal access to school.